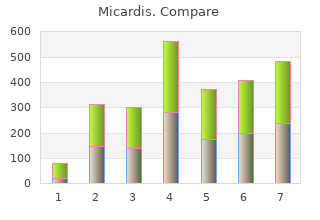
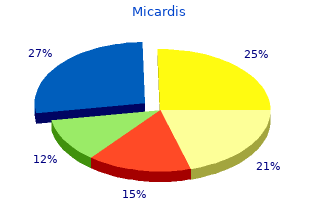
Micardis
By R. Quadir. Otterbein College. 2018.
The zygomatic arch and part of the mandible have been removed to reveal the medial and lateral pterygoid muscles micardis 20 mg lowest price 4 arteria aorta. Radially arranged muscles work as Left side: superficial layer 80mg micardis amex hypertension headache, right side: deeper layer. Maxillary Artery 63 1 Galea aponeurotica 2 Superficial temporal artery and auriculo- temporal nerve 3 Occipital artery and greater occipital 1 12 nerve (C2) 4 Temporomandibular joint (opened) 5 External carotid artery 13 6 Mandible and inferior mandibular artery and 2 nerve 14 7 Accessory nerve (Var. I) pass the lamina cribrosa innervating the upper part of the nasal mucous membrane. Brain, brain stem, of the neck, the tongue, and the and cerebellum have been partly removed (from Lütjen-Drecoll, Rohen, Innenansichten des pharynx. V) Brain and Cranial Nerves 67 Brain stem and pharynx with cranial nerves (posterior aspect). Lateral wall of cranial cavity, lateral wall of orbit, zygomatic arch, and ramus of the mandible have been removed and the mandibular canal opened. V2) 2 Supra-orbital nerve pterygopalatine nerves 24 Trigeminal ganglion 3 Lacrimal nerve 13 Posterior superior alveolar 25 Mandibular nerve (n. V3) 4 Lacrimal gland nerves 26 Auriculotemporal nerve 5 Eyeball 14 Superior dental plexus 27 External acoustic meatus (divided) 6 Optic nerve and short ciliary nerves 15 Buccinator muscle and buccal nerve 28 Lingual nerve and chorda tympani 7 External nasal branch of 16 Inferior dental plexus 29 Mylohyoid nerve anterior ethmoidal nerve 17 Mental foramen and mental nerve 30 Medial pterygoid muscle 8 Ciliary ganglion 18 Anterior belly of digastric muscle 31 Inferior alveolar nerve 9 Zygomatic nerve 19 Ophthalmic nerve (n. V1) 32 Posterior belly of digastric muscle 10 Infra-orbital nerve 20 Oculomotor nerve (n. V3) 12 Posterior superior alveolar nerves 13 Tympanic cavity, external acoustic meatus, and tympanic membrane 14 Inferior alveolar nerve 15 Lingual nerve 16 Facial nerve (n. Facial canal and tympanic cavity opened, posterior wall of external acoustic meatus removed. Branches of facial nerve: a = temporal branch; b = zygomatic branches; c = buccal branches; d = marginal mandibular branch. The mandible has been divided and the muscles of mastication have been Facial nerve (schematic drawing of the dissection above). Brain and Cranial Nerves: Connection with the Brain Stem 71 1 1414 2 3 15 16 4 17 5 18 6 19 20 7 8 21 22 9 10 23 24 11 25 26 27 12 28 13 18 29 1 Optic tract 11 Lingual branch of hypoglossal nerve 22 Hypoglossal nerve (n. V) 27 Sympathetic trunk 7 Lingual nerve and inferior alveolar nerve 17 Fourth ventricle and rhomboid fossa 28 Branch of cervical plexus (ventral 8 Styloid process and stylohyoid muscle 18 Vagus nerve (n. V3) 7 23 26 External acoustic meatus 8 21 27 Pterygopalatine nerves 24 28 Deep temporal nerves 10 25 29 Buccal nerve 30 Masseteric nerve 11 31 Auriculotemporal nerve 32 Trochlea and superior oblique muscle 16 Cranial nerves innervating extra-ocular muscles (lateral aspect). Right side: superficial layer, left side: middle layer of the orbit (superior rectus muscle and frontal nerve divided and reflected). V1) 19 Optic chiasma and internal carotid artery 20 Trigeminal ganglion 21 Trigeminal nerve (n. V) 22 Tentorial notch 23 Superior rectus muscle Cranial nerves within the orbit (superior aspect). V) 11 Cerebellum 12 Eyeball 13 Medial and lateral rectus muscles 14 Internal carotid artery 15 Oculomotor nerve (n. Brain and Cranial Nerves: Base of the Skull with Cranial Nerves 75 Base of the skull with cranial nerves (internal aspect). Incision on the right tentorium cerebelli to display the cranial nerves of the infratentorial space. Regions of the Head: Lateral Region 77 1 Temporoparietalis muscle 2 Superficial temporal artery and vein, and auriculotemporal nerve 2 3 Occipital belly of occipitofrontalis muscle and greater occipital nerve (C2) 27 4 Facial nerve (n. Retromandibular and submandibular regions of the head 31 Anterior belly of digastric (lateral aspect). The parotid plexus (4) is formed by anastomosis of the temporal, zygomatic, buccal, marginal mandibular, and cervical branches of the facial nerve, arising in the parotid gland. Masseter muscle and temporal fascia have been partly removed to display the masseteric artery and nerve. The coronoid process together with the insertions of temporalis muscle have been removed to display the maxillary artery.
Treating infection The antibiotic era has witnessed many microorganism mutations cheap 20mg micardis amex heart attack trey songz lyrics, creating resistance to successive generations of (increasingly expensive and toxic) antibiotics generic 20 mg micardis mastercard hypertension facts. Drug companies face escalating investment costs for products increasingly difficult to market, and potentially soon obsolete; Gould (1994b) reports that one-half of drug companies are stopping or seriously reducing antibiotic production. The Chief Medical Officer for Scotland has predicted that by 2020 healthcare will run out of antibiotics (cited by Amyes & Thomson 1995). Such statements may appear sensationalist, but they emphasise the need to reorientate from relying on drugs to preventing and controlling infection. Antibiotics remain useful adjuncts to treatment, but will probably become progressively less effective. The inappropriate use of antibiotics has created more pathogenic, resistant organisms (Parke & Burden 1998), and so unnecessary use is actively discouraged (House of Lords Select Committee on Science and Technology 1998). Early onset pneumonia (from aspiration during trauma) is usually antibiotic- sensitive, but late onset pneumonia (ventilator-associated pneumonia) is usually resistant (Rello et al. Monoclonal antibodies are cloned and genetically engineered human Blymphocytes (Eburn 1993). Heat Moisture Exchangers) should be changed according to manufacturers’ instructions (normally daily); catheter mounts should be changed at the same time as humidifiers Infection control 135 ■ invasive techniques and disconnection of intravenous lines should, when possible, avoid times of dust disturbance (e. Antibiotics and other medical treatments can reduce morbidity and mortality, but preventing infection is humanly (and usually financially) preferable. Hygiene is helped by adequate and appropriate facilities, including sufficient washbasins, aprons and unit guidelines and protocols. All multidisciplinary team members should be actively involved in making decisions, but nurses have an especially valuable role in coordinating and controlling each patient’s environment. Problems from infection are likely to escalate; continuing vigilance and care can minimise infection risks and the spread of microorganisms. Further reading Articles on infection control frequently appear in specialist and general journals. Taylor’s (1978) classic article on handwashing is recommended; issues for nursing practice regularly appear in many general nursing journals. She was transferred from elderly care facilities with rapidly deteriorating respiratory function, copious mucopurulent sputum and atelectasis. Catherine’s previous respiratory tract infections had been treated with oral Amoxycillin (beta lactam class of antibiotics). Issues related to infection control are included in end-of-chapter scenarios in chapters 39 and 40. Chapter 16 Ethics Introduction The value of ethics for healthcare has been increasingly recognised: critical care often adds greater focus and poignancy to ethical dilemmas. Ethics raises questions rather than provides answers; dilemmas have more than one solution. Each person has values; some are formed or shared with peer groups, others are individual. Different values may cause conflict (for example, the care versus cure debate of Chapter 1). Active questioning enables evaluation of beliefs underpinning practice, helping nurses to understand others’ perspectives, but solutions necessarily remain individual. Increasing public expectations (and litigation) of healthcare, and changes within nursing (increased autonomy, responsibility and accountability) are reflected by greater emphasis on ethics in nursing education. A high public and media profile makes intensive care nursing a much-scrutinized area. This chapter provides a basis both for practice and for the remainder of this book; professional development can usefully be extended through discussion with colleagues and further study. This chapter describes the four main ethical principles identified by Beauchamp and Childress (1994): ■ autonomy ■ non-maleficence ■ beneficence ■ justice and the three main ethical theories identified by Rumbold (1993): ■ duty-based ■ goal-based ■ rights-based Other authors may give different arrangements, wording or additional theories and principles. Ethical principles provide a framework with which to work through dilemmas, identifying what is harmful, what is good and what is just.
We are not told whether he had a fever discount 80mg micardis mastercard arrhythmia yahoo answers, and the white cell count should be measured discount 40 mg micardis free shipping heart attack sam. If this does seem the likely diagnosis it would be best to treat him where he is, if this is safe and possible. There is every likelihood that he will return to his previous state if the urinary tract infection is confirmed and treated appropriately, although this may take longer than the response in temperature and white cell count. Treatment should be started on the pre- sumption of a urinary tract infection, while the diagnosis is confirmed by microscopy and culture of the urine. The most likely organism is Escherichia coli, and an antibiotic such as trimethoprim would be appropriate, although resistance is possible and advice of the local microbiologist may be helpful. From the confusion point of view he should be treated calmly, consistently and without confrontation. If medication is necessary, small doses of a neuroleptic such as haloperidol or olanzapine would be appropriate. In dementia, there is an acquired global impairment of intellect, memory and personality, but consciousness is typically clear. She had last seen him at 8 pm the evening before when they came home after Christmas shopping. When she came to see him the next afternoon she found him unconscious on the floor of the bathroom. There was a family history of diabetes mellitus in his father and one of his two brothers. His girlfriend had said that he had shown no signs of unusual mood on the previous day. He had his end of term examinations in psychology coming up in 1 week and was anx- ious about these but his studies seemed to be going well and there had been no problems with previous examinations. The first part of the care should be to ensure that he is stable from a cardiac and respiratory point of view. Blood gases should be measured to monitor the oxy- genation and ensure that the carbon dioxide level is not high, suggesting hypoventilation. The family history of diabetes raises the possibility that his problem is related to this. One would expect a slower development with a history of thirst and polyuria over the last day or so. Hypoglycaemia comes on faster but would not occur as a new event in diabetes mellitus. Other metabolic causes of coma such as abnormal levels of sodium or calcium should be checked. A neurological problem such as a subarachnoid haemorrhage is possible as a sudden unexpected event in a young person. Where the level of consciousness is so affected, some localizing signs or subhyaloid haemorrhage in the fundi might be expected. Despite the lack of any warning of intent beforehand, drug overdose is common and the question of avail- ability of any medication should be explored further. If there is any suspicion of this then levels of other drugs which might need treat- ment should be measured, e. The other possibility in somebody brought in unconscious is that they are suffering from carbon monoxide poisoning. The fact that it is winter and he was found in the bathroom where a faulty gas-fired heater might be situated increases this possibility. Patients with carbon monoxide poisoning are usually pale rather than the traditional cherry-red colour associated with carboxyhaemoglobin. Papilloedema can occur in severe carbon monoxide poisoning and might account for the swollen appearance of the optic discs on funduscopy. He was treated with high levels of inspired oxygen and made a slow but full recovery over the next 48 h. Mannitol for cerebral oedema and hyperbaric oxygen are considerations in the management. The problem was traced to a faulty gas water heater which had not been serviced for 4 years. His conscious level is decreased but he is rousable to command and there are no focal neurological signs.
The axes remind us that when making a diagnosis we must look at the complete picture buy micardis 20mg free shipping arrhythmia death, including biological purchase 40mg micardis otc heart attack chords, personal, and social-cultural factors. For instance, the disorder of mental retardation can be classified as mild, moderate, or severe. In school, he cannot stay in his seat for very long and he frequently does not follow instructions. Zack has poor social skills and may overreact when someone accidentally bumps into him or uses one of his toys. At home, he chatters constantly and rarely settles down to do a quiet activity, such as reading a book. Symptoms such as Zack‘s are common among 7-year-olds, and particularly among boys. Boys mature more slowly than girls at this age, and perhaps Zack will catch up in the next few years. One possibility is for the parents and teachers to work with Zack to help him be more attentive, to put up with the behavior, and to wait it out. But many parents, often on the advice of the child‘s teacher, take their children to a psychologist for diagnosis. Other studies have also pointed to environmental factors, such as mothers‘ smoking and drinking alcohol during pregnancy and the consumption of lead and food additives by those who are affected (Braun, Kahn, Froehlich, [23] Auinger, & Lanphear, 2006; Linnet et al. Jared is able to maintain eye contact and enjoys mixing with other children, but he cannot communicate with them very well. He often responds to questions or comments with long-winded speeches about trucks or some other topic that interests him, and he seems to lack awareness of other children‘s wishes and needs. Jared‘s concerned parents took him to a multidisciplinary child development center for consultation. Here he was tested by a pediatric neurologist, a psychologist, and a child psychiatrist. The pediatric neurologist found that Jared‘s hearing was normal, and there were no signs of any neurological disorder. He diagnosed Jared with a pervasive developmental disorder, because while his comprehension and expressive language was poor, he was still able to carry out nonverbal tasks, such as drawing a picture or doing a puzzle. Based on her observation of Jared‘s difficulty interacting with his peers, and the fact that he did not respond warmly to his parents, the psychologist diagnosed Jared with autistic disorder (autism), a disorder of neural development characterized by impaired social interaction and communication and by restricted and repetitive behavior, and in which symptoms begin before 7 years of age. The psychologist believed that the autism diagnosis was correct because, like other children with autism, Jared, has a poorly developed ability to see the world from the perspective of others; engages in unusual behaviors such as talking about trucks for hours; and responds to stimuli, such as the sound of a car or an airplane, in unusual ways. The child psychiatrist believed that Jared‘s language problems and social skills were not severe enough to warrant a diagnosis of autistic disorder and instead proposed a diagnosis of Asperger‘s disorder, a developmental disorder that affects a child’s ability to socialize and Attributed to Charles Stangor Saylor. The symptoms of Asperger‘s are almost identical to that of autism (with the exception of a delay in language development), and the child psychiatrist simply saw these problems as less extreme. Clearly there is something wrong with their child, but even the experts cannot agree on exactly what the problem is. Diagnosing problems such as Jared‘s is difficult, yet the number of children like him is increasing dramatically. Disorders related to autism and Asperger‘s disorder now affect almost 1% of [25] American children (Kogan et al. The milder forms of autism, and particularly Asperger‘s, have accounted for most of this increase in diagnosis. Although for many years autism was thought to be primarily a socially determined disorder, in which parents who were cold, distant, and rejecting created the problem, current research suggests that biological factors are most important. The heritability of autism has been estimated [26] to be as high as 90% (Freitag, 2007). Scientists speculate that autism is caused by an unknown genetically determined brain abnormality that occurs early in development. It is likely [27] that several different brain sites are affected (Moldin, 2003), and the search for these areas is being conducted in many scientific laboratories.
8 of 10 - Review by R. Quadir
Votes: 196 votes
Total customer reviews: 196

Detta är tveklöst en av årets bästa svenska deckare; välskriven, med bra intrig och ett rejält bett i samhällsskildringen.
Lennart Lund